Understanding freight shipping can feel overwhelming due to the wide range of industry-specific terms used daily. Whether you’re a business owner shipping products or an individual sending goods, grasping key freight shipping terms can help you navigate the process with confidence. In this blog, we’ll break down 25 essential freight shipping terms that you should know to streamline your shipping experience.
1. Bill of Lading (BOL)
A critical legal document between the shipper and the carrier that outlines the details of the shipment, such as the type, quantity, and destination of goods. It serves as a receipt and contract for transportation.
2. Freight Class
Freight class is a system used to categorize shipments based on factors like weight, size, density, and value. It helps standardize pricing for Less Than Truckload (LTL) shipping.
3. Dimensional Weight (DIM Weight)
This refers to a pricing model used by carriers where both the size and weight of the shipment are considered. Larger, lighter packages may be charged based on their dimensions rather than their actual weight.
4. Less Than Truckload (LTL)
LTL shipping is used when a shipment doesn’t require the full space of a truck. This method allows multiple shippers to share truck space, reducing costs.
5. Full Truckload (FTL)
In FTL shipping, an entire truck is reserved for a single shipment. This is ideal for large or high-volume shipments that require more space.
6. Freight Forwarder
A freight forwarder is a company or agent that arranges shipping services on behalf of shippers. They handle logistics, documentation, and can even provide customs clearance services.
7. Pallet
A pallet is a flat wooden or plastic platform used to stack and transport goods. Palletizing shipments makes loading and unloading easier and protects goods during transport.
8. Accessorial Charges
These are additional fees added to the basic freight charge. Accessorials may include services like liftgate delivery, inside delivery, or fuel surcharges.
9. Customs Broker
When shipping internationally, a customs broker facilitates the clearance of goods through customs. They ensure compliance with laws and handle duties and taxes on behalf of the shipper.
10. Carrier
A carrier is the company responsible for physically transporting goods from one place to another, whether by truck, ship, air, or rail.
11. Freight Rate
This refers to the charge applied by the carrier to move goods. Freight rates are influenced by factors like weight, distance, mode of transport, and freight class.
12. Pro Number
A unique identification number assigned to a shipment for tracking purposes. It allows shippers and carriers to track the location and status of the freight.
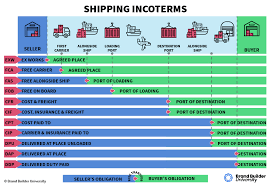
13. Incoterms
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers for the transportation and delivery of goods in international trade.
14. Freight Consolidation
This is the practice of combining smaller shipments from multiple shippers into a single load. This reduces shipping costs, especially for LTL shipments.
15. Deadhead
A term used when a truck returns to its origin point empty after completing a delivery. Deadheading can increase costs since the truck isn’t transporting revenue-generating freight.
16. Flatbed Truck
A flatbed truck has no sides or roof, making it ideal for transporting large, heavy, or awkwardly shaped goods that wouldn’t fit in a standard truck.
17. Freight Claim
When goods are damaged or lost in transit, the shipper or consignee can file a freight claim to seek compensation from the carrier.
18. Hazmat
Hazardous materials (Hazmat) are substances that pose a risk to health, safety, or the environment. Shipping Hazmat requires special handling and documentation.
19. Dock
A dock is the area where trucks are loaded and unloaded at shipping facilities, warehouses, or distribution centers.
20. Drop Shipment
In a drop shipment, goods are shipped directly from the manufacturer or supplier to the customer, bypassing the seller’s physical location. This saves time and reduces handling.
21. Intermodal Shipping
Intermodal shipping refers to the use of multiple forms of transportation—such as truck, rail, and ship—to move goods from origin to destination.
22. Lead Time
Lead time is the total time it takes from placing an order to when the goods are delivered. This includes production, packaging, and shipping time.
23. Reefer
A reefer is a refrigerated container or truck used to transport temperature-sensitive goods like food, pharmaceuticals, and other perishable items.
24. Tariff
A tariff is a tax or duty imposed on imports or exports. Understanding tariffs is crucial when shipping goods internationally.
25. Volumetric Weight
Also known as dimensional weight, volumetric weight is calculated based on the size of the package rather than its actual weight. Carriers use this for large, lightweight shipments to ensure fair pricing.
Conclusion
Freight shipping doesn’t have to be complicated. By understanding these 25 key terms, you’ll be better equipped to communicate with carriers, avoid costly mistakes, and manage your shipping needs efficiently. Whether you’re shipping domestically or internationally, being familiar with these terms will help make the process smoother and more cost-effective.